Revolutionizing Genetic Engineering and Beyond
In recent years, the field of genetics has witnessed a groundbreaking advancement known as CRISPR. This revolutionary technology has captivated scientists and researchers worldwide, offering a precise and efficient method for editing genes. CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) has the potential to transform various fields, from healthcare and agriculture to environmental conservation. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of CRISPR, its applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding its use.
source: https://www.genengnews.com/news/paste-expands-crispr-toolbox-by-inserting-large-pieces-of-dna/
Understanding CRISPR:
CRISPR is a gene-editing tool that utilizes a naturally occurring defense mechanism found in bacteria. It consists of two key components: a guide RNA (gRNA) and an enzyme called Cas9. The gRNA is designed to target a specific DNA sequence, guiding Cas9 to the desired location within the genome. Once at the target site, Cas9 acts as molecular scissors, cutting the DNA strand. This break triggers the cell’s repair mechanisms, which can be harnessed to introduce precise genetic modifications.
source https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/mrs-bulletin/news/crispr-implications-for-materials-science
Applications in Healthcare:
CRISPR holds immense potential in the field of healthcare. It offers the possibility of treating genetic disorders by correcting or modifying problematic genes. Researchers are exploring the use of CRISPR for conditions such as sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and certain types of cancers. Additionally, CRISPR-based diagnostics are being developed to detect infectious diseases and identify genetic markers associated with specific conditions, enabling early detection and personalized medicine.
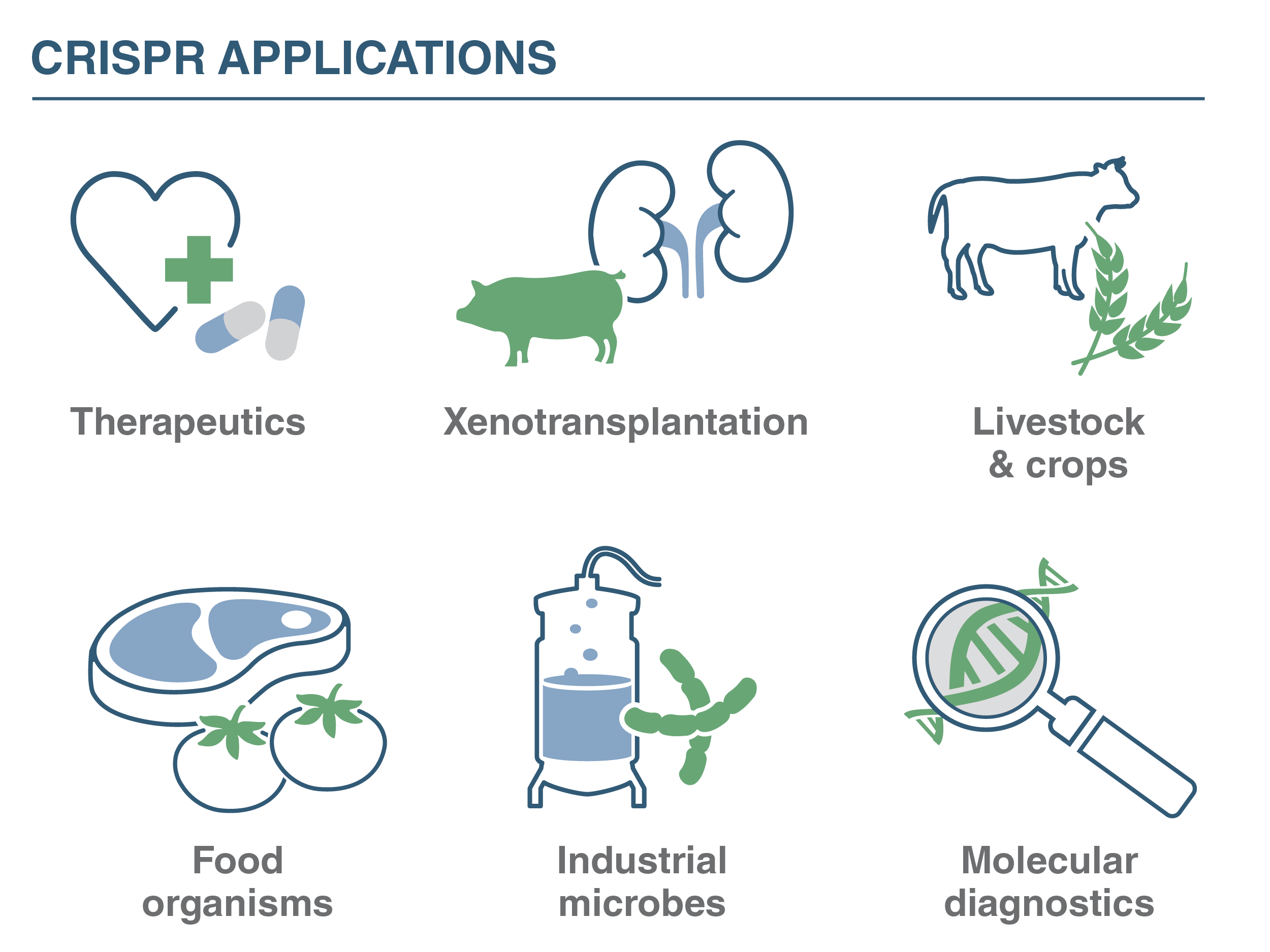
source: https://www.neb.com/en/nebinspired-blog/adding-capabilities-to-crispr-cas-based-biotechnology
Agricultural Advancements:
CRISPR has significant implications for agriculture and food production. It allows scientists to develop crop varieties with improved traits, such as increased yield, enhanced nutritional value, and resistance to pests, diseases, or environmental stress. By precisely modifying plant genomes, CRISPR can expedite the breeding process and potentially address challenges related to food security and sustainability. However, regulatory considerations and public acceptance remain important factors in the adoption of CRISPR-edited crops.
Environmental Conservation:
CRISPR also offers opportunities for environmental conservation and ecological restoration. Scientists are exploring the use of gene editing to mitigate the impacts of invasive species, combat disease outbreaks in wildlife populations, and conserve endangered species. However, the application of CRISPR in the wild raises ethical questions and requires careful consideration of potential ecological consequences.
Ethical Considerations:
The immense power of CRISPR raises ethical considerations that must be addressed. One major concern is the potential for off-target effects, where unintended genetic modifications occur. Scientists are continually refining CRISPR techniques to minimize off-target effects and enhance precision. Additionally, the germline editing of human embryos, which raises ethical and societal questions, remains a topic of debate and is subject to strict regulations in many countries.
 source https://thevarsity.ca/2021/09/04/crispr-gene-editing-ethical-dilemma/
source https://thevarsity.ca/2021/09/04/crispr-gene-editing-ethical-dilemma/
Regulatory Landscape:
The regulatory landscape surrounding CRISPR is evolving. Different countries have varying policies and guidelines regarding the use of CRISPR in research, medicine, and agriculture. It is essential to strike a balance between facilitating scientific progress and ensuring responsible and ethical use of this technology.
Conclusion:
CRISPR has emerged as a game-changing technology with vast implications for various fields. Its potential to edit genes with precision and efficiency opens doors to new possibilities in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental conservation. However, it is crucial to proceed with caution, addressing ethical concerns, refining techniques, and navigating the regulatory landscape. With responsible use and ongoing advancements, CRISPR has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of genetics and shape the future of our world.